This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
The Complete Guide to Initializing Arrays in Java
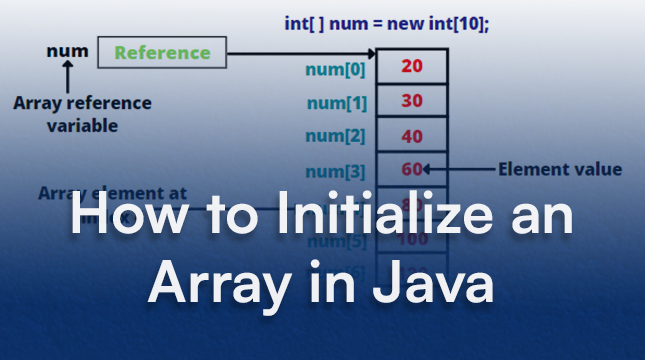
Java arrays are data structures of a fixed size. The most important process is initializing arrays in Java, which involves allocating memory for the array and (optionally) assigning initial values. Failing to properly initialize an array reference in Java will result in a compilation error if you try to use it.
In Java programming, there are four major and unique ways of array initiation, each with its unique meaning.
Method 1: The Three-Step Process (Declaration, Allocation, and Assignment)
This method is the least implicit, and it clearly illustrates how the definition of the reference, reservation of memory, and assigning values are clearly distinct. You generally use this method when the size is known but the values will be determined later, usually within a loop or from user input.
Step 1: Declaration
You declare the array reference variable, defining the data type of the elements it will hold.
int[] studentScores;
// or the less common C-style
String names[];
Step 2: Allocation (Instantiation)
You use the new keyword to instantiate the array object, reserving a contiguous block of memory on the heap and specifying the array’s fixed size.
// Reserves space for 5 integers
studentScores = new int[5];
Memory and Default Values
When you allocate memory, Java guarantees that all array elements are automatically initialized to a default value corresponding to their data type. This prevents unexpected behavior from uninitialized memory locations.
- Numeric Types (int, double, etc.): 0
- boolean: false
- char: ′0˘000′ (The Null character)
- Reference Types (String, Objects): null
Step 3: Explicit Assignment
You manually assign values to specific indices, where indices range from 0 to length−1.
studentScores[0] = 95; // The first element
studentScores[1] = 88;
// ...
studentScores[4] = 92; // The last element
Attempting to access studentScores[5] would result in an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException at runtime, as the maximum index is 4.
Method 2: The Array Initializer Block
This method is the preferred way of initializing arrays in Java when all array elements are known at the time of declaration, combining declaration, allocation, and initialization in a single, concise statement.
Here, the new data type [size] part is omitted, and the Java compiler implicitly assigns the size depending on the number of values given in the curly braces.
// The size is automatically set to 4
String[] flavors = {"Vanilla", "Chocolate", "Strawberry", "Mint"};
// The size is automatically set to 5
double[] percentages = {10.5, 20.0, 33.3, 40.0, 50.0};
Method 3: Using the new Keyword with an Initializer Block
This method is a hybrid: it uses the array initializer block but also explicitly includes the new dataType[] keyword. While less common for simple declarations, it’s necessary for creating anonymous arrays.
// Explicitly using 'new'
char[] letters = new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C'};
The Power of Anonymous Arrays
You create and initialize an anonymous array without assigning it to a reference variable. Since it has no name, you can use it only immediately after creation, typically when passing temporary data to a method.
// Define a method that accepts an array
public static int getSum(int[] data) {
int sum = 0;
for (int value : data) {
sum += value;
}
return sum;
}
// Pass an anonymous array to the method
int total = getSum(new int[]{5, 10, 15, 20});
System.out.println("Total: " + total);
Output:
4. Initializing Multidimensional Arrays
You initialize multidimensional arrays (arrays of arrays, commonly 2D) using nested braces.
A. Initialization with Known Values
For a standard matrix structure, you nest the initializer blocks:
// A 3x3 matrix (3 rows, 3 columns)
int[][] matrix = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6},
{7, 8, 9}
};
// Access: matrix[1][2] is 6 (Row 1, Column 2)
B. Initializing Jagged Arrays (Arrays of Unequal Length)
Java allows the sub-arrays to have different lengths; these are called jagged arrays. You must specify the size of the first dimension (the number of rows), but you can leave the second dimension blank.
// 1. Specify 3 rows, but leave column sizes open
int[][] jaggedArray = new int[3][];
// 2. Initialize each row separately with its own size/values
jaggedArray[0] = new int[]{10, 20, 30}; // Length 3
jaggedArray[1] = new int[]{40, 50}; // Length 2
jaggedArray[2] = new int[]{60, 70, 80, 90}; // Length 4
// Access: jaggedArray[1].length is 2
Also Read: Increment and decrement operators in Java
Summary of Initialization Techniques
| Method | Syntax | Memory Allocation | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Separate Steps | int[] a = new int[5]; a[0] = 1; | Explicitly requires size definition. | Size is known, but values are assigned dynamically (e.g., from user input or calculation). |
| Initializer Block | int[] a = {1, 2, 3}; | Implicitly sized by the compiler. | Values are fixed and known at the time of coding. (Recommended) |
| Anonymous Array | method(new int[]{1, 2}); | Implicitly sized by the compiler. | Passing a temporary array as a method argument without creating a persistent variable. |
By mastering these techniques for initializing arrays in Java, you ensure your programs handle array memory and data correctly, avoiding common pitfalls like NullPointerException and ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.

Let's Start Your Project
Get free consultation for your digital product idea to turn it into reality!
Get Started