This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
What is the Difference Between AI and AGI?
You’ve undoubtedly heard the terms AI and AGI used interchangeably if you’ve been reading tech news or discussing the newest devices with friends. But believe me, they aren’t, and realizing the distinction can significantly alter your perspective on how technology will develop in the future.
Think of AGI as your super-smart coworker who could manage your entire job (and perhaps even create a new one), while AI is your dependable smartphone assistant that reminds you of meetings. We’ll explore what makes them unique in this post in an easy-to-understand manner. Stay tuned, whether you’re a business owner considering AI tools or you’re simply interested in the future of technology.
I’ll give a conversational explanation supported by some startling statistics. You’ll feel like an authority by the end, prepared to contribute to the discussion.
Shall we begin with the fundamentals?
What Exactly is AI?
Imagine this: You’re using Siri to set an alarm or Netflix suggesting your next binge-watch. That’s artificial intelligence or more specifically, AI as action. Fundamentally, artificial intelligence (AI) refers to computer programs created to carry out particular tasks that normally call for human intelligence, such as pattern recognition, prediction, or language processing.
Because they are experts in one area but ignorant of others, these systems are “narrow.” Deep Blue, for instance, is an AI that can beat grandmasters at chess, but it is unable to teach you how to drive or bake a cake.
AI works through algorithms, often powered by machine learning, where the system learns from massive datasets. Think of it as training a dog to fetch, lots of repetition until it gets it right for that one trick. Today, AI is everywhere, from chatbots handling customer service to algorithms detecting fraud in banking. If you’re looking to integrate something like AWS Generative AI into your apps for that extra edge, check out this guide on integrating AWS Generative AI into your applications. It’s a game-changer for businesses wanting to automate without the hassle.
But here’s the kicker: AI needs humans to define its goals and feed it data. Without that, it’s just code sitting idle.
What About AGI? The Next Level Up
Let’s step it up to Artificial General Intelligence, or AGI. Depending on who you ask, this is the stuff of sci-fi nightmares or dreams. AGI is a system that can comprehend, learn, and apply knowledge across any intellectual challenge that a human can manage; it is not task-specific. Imagine a single artificial intelligence (AI) that could fix your car’s engine, compose a symphony, negotiate a business deal, and diagnose a medical condition, all without requiring retraining for each task.
AGI would be more creative, flexible, and able to reason like a human than current AI. In the same way that you might improvise a new recipe using what you know, it might use general knowledge to solve unfamiliar problems. AGI is still in the research stage at this time; no real AGI has been created, but businesses like OpenAI and xAI are pushing the envelope. For a deeper look at how AI is evolving globally, you might enjoy this piece on the emergence of AI and how it’s changing the world.
The crucial query? When will AGI be available? Experts predict that it will have a 25% chance by 2027 and a 50% chance by 2031. Others, such as Sam Altman of OpenAI, have made aggressive timelines that suggest it might happen as early as 2025. Sounds exciting, doesn’t it? However, it also brings up moral issues that we will discuss later.
Key Differences Between AI and AGI: Breaking It Down
Now, how do these two actually compare? Let’s use a straightforward analogy to clarify this. Since everyone enjoys a good visual aid, I’ll use a table in this instance. (Pro tip: This infographic, which shows a side-by-side flowchart of AI vs. AGI capabilities, will increase engagement and aid with SEO if you’re creating content similar to this.)
See the gap? AI is like a specialist doctor, while AGI is the ultimate general practitioner who knows it all. If you’re into tools that bridge this gap, explore the best AI tools to help you work and create, they’re perfect for everyday productivity without waiting for AGI.
Eye-Opening Statistics and Trends: The Numbers Don’t Lie
Nothing is more convincing than hard, unvarnished facts, so let’s support this with some actual data. These figures demonstrate how quickly things are developing in the rapidly expanding field of artificial intelligence.
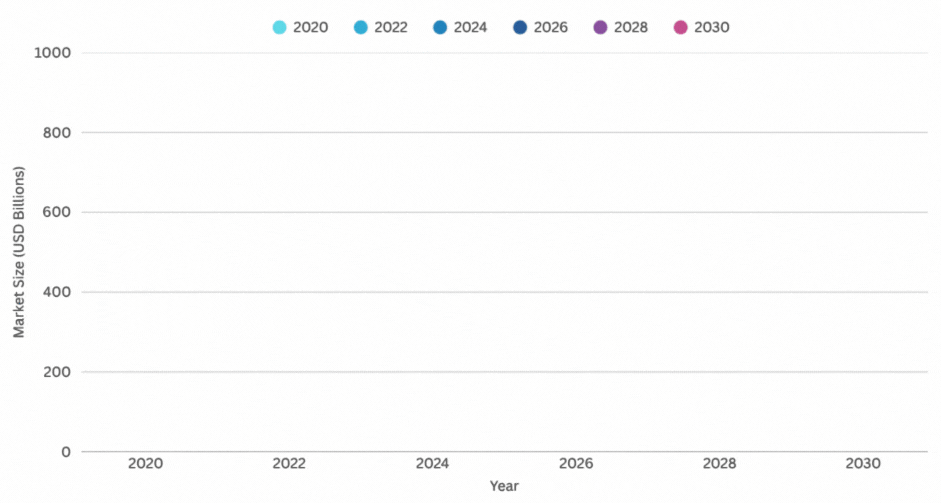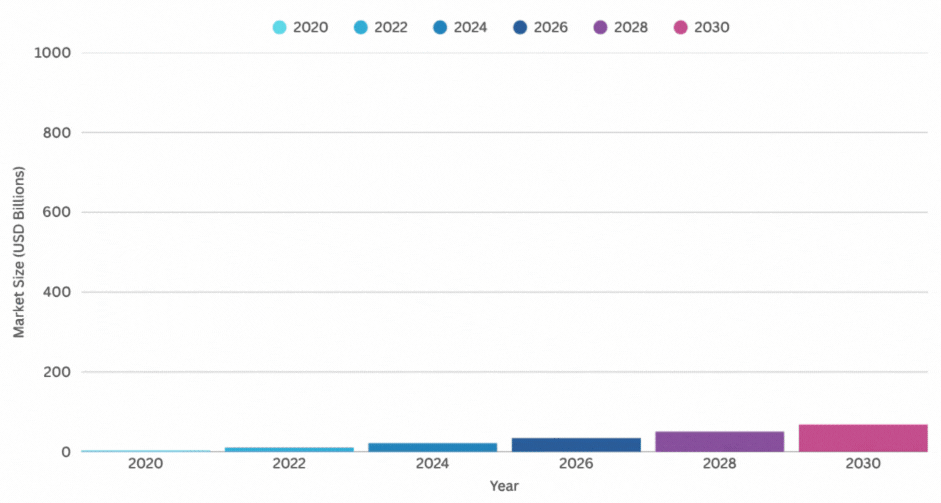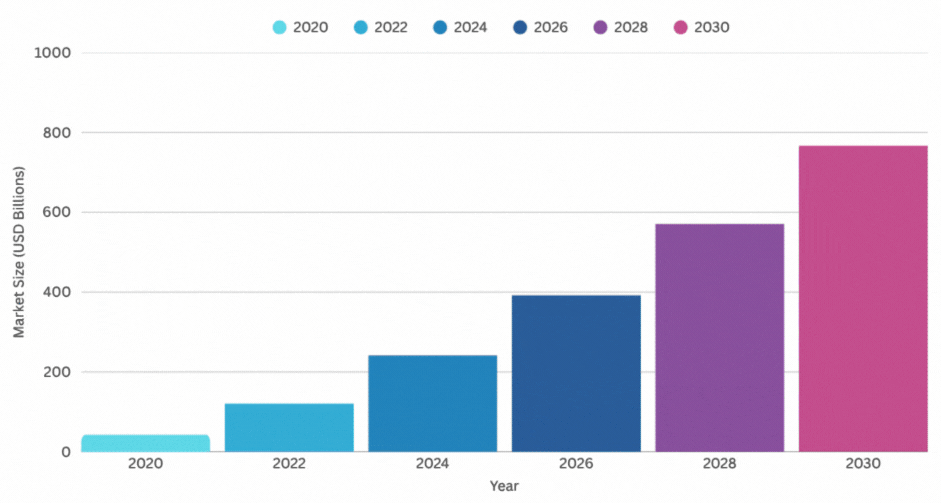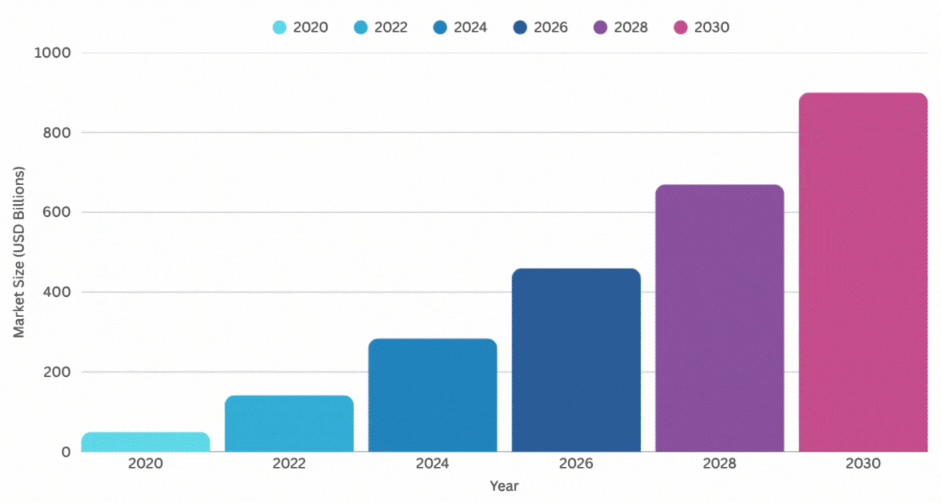
- The global AI market is projected to hit around $371.71 billion in 2025, growing at a blistering pace from previous years. That’s up from about $184 billion in 2024, showing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 29%.
- On adoption: A whopping 78% of organizations now use AI in at least one business function in 2025, jumping from 72% last year. In the US, 40% of employees report using AI at work, double from 2023.
If AGI timelines intrigue you, surveys show a median prediction of AGI by 2040-2060, but recent buzz shortens it for some. For more on rewriting content with AI (a narrow but useful application), try this AI rewriter guide.
Why Does This Difference Matter? Real-World Implications
Understanding AI vs. AGI isn’t just academic, it’s about preparing for what’s next. AI is already transforming jobs, like automating routine tasks in marketing or customer support. (Speaking of which, if you want to build your own chatbot, learn about the benefits of making AI chatbots by integrating GPT-3.) But AGI could reshape entire industries, solving complex problems like climate change or drug discovery overnight.
On the flip side, there are risks: AI can have biases, while AGI might lead to ethical dilemmas around control and job loss. For external insights, check out OpenAI’s official stance on AGI development here or dive into Wikipedia’s comprehensive page on Artificial General Intelligence for a neutral overview.
Also, if you’re into creative AI, don’t miss Bing AI art or the Bing AI image generator, fun ways to experiment with narrow AI today. And for quick responses, an AI response generator can save you time.
Wrapping It Up: Your Takeaway on AI vs. AGI
That concludes the main distinction between specialization and versatility. While AGI promises a world of limitless potential (with some limitations), AI is currently our powerhouse for targeted efficiency. Keep an eye out for breakthroughs as 2026 draws nearer, they’re happening more quickly than ever before.
What do you think? Is AGI a boon or a risk? Drop a comment below, and if this sparked your interest, share it with a friend. For more AI goodness, explore the links above or head to reliable sources like Stanford’s AI Index for annual reports.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between AI and AGI?
The scope is where AI and AGI diverge most. Artificial intelligence, or AI, is limited and only performs well at certain tasks, such as image processing or voice recognition (e.g., Netflix recommendations or Siri). Artificial General Intelligence, or AGI, is a theoretical system that can complete any intellectual task that a human can, adapting to different domains such as creativity, reasoning, and problem-solving without the need for retraining.
2. Can you give examples to explain the difference between AI and AGI?
Yes! AI powers self-driving car features like lane detection and writing tools like ChatGPT. These vary depending on the task. AGI, which does not yet exist, would be similar to a single system that could simultaneously manage a business, diagnose illnesses, and write a novel. Narrow focus versus human-like versatility is the primary distinction between AI and AGI.
3. Is AGI available now, and how does it compare to AI in development?
No, artificial general intelligence is still a research goal for firms like xAI and OpenAI. By 2025, 78% of businesses will have implemented AI for tasks like automation. In terms of development, AI and AGI differ in that AI relies on pre-existing algorithms, whereas AGI necessitates advances in general reasoning and flexibility.
4. Why is understanding the difference between AI and AGI important?
Understanding the distinction between AI and AGI enables you to appreciate both their advantages and disadvantages. While AI increases productivity in sectors like healthcare and finance, artificial general intelligence (AGI) has the potential to transform entire industries, such as addressing climate change. However, it’s important to remain informed because AGI also brings up ethical issues like control or job displacement.
5. When might we see AGI, and how does it relate to current AI?
While some experts predict a 50% chance of AGI by 2031, others predict 2040 or later. The difference between AI and AGI is that the latter would require human-like flexibility, which we are still a long way from achieving. Current AI, such as chatbots or image generators (check out Bing AI art), is a stepping stone.
6. Are there risks associated with the difference between AI and AGI?
Indeed! By 2025, 40% of US workers will be utilizing AI, and risks include biases and job automation. There are greater risks associated with AGI, such as possible loss of control or misalignment with human values. The scale of the risks posed by AGI differs from that of AI; its effects may be widespread.
7. How can businesses use the difference between AI and AGI to plan ahead?
With tools like AI chatbots that use GPT-3, businesses can now use AI for tasks like customer support. They can better prepare for AGI’s potential to disrupt industries by automating complex decision-making and staying competitive by knowing the difference between AI and AGI.
8. Where can I learn more about tools related to AI and AGI?
Investigate the top AI tools available to assist you in your work and develop or test an AI response generator. See the emergence of AI or outside resources such as OpenAI’s AGI page for more general trends.

Let's Start Your Project
Get free consultation for your digital product idea to turn it into reality!
Get Started