This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Understanding Network Topology: A Comprehensive Guide
Written by
NetizensJanuary 27, 2025
14 min read
What is network topology, and why do the different types of it matter? Network topology is the way that computers, routers, switches, and other devices are set up and connected in a computer network. It’s the blueprint that controls how data moves, which affects everything from the speed of the network to its dependability. If you want to understand how networks work, you need to know about network topology. This is true whether you are a student studying for an IT certification, a network administrator designing a system, or a beginner learning about computer networking.
This guide goes into great detail about network topology, including what it is, the different types, diagrams, and how it is used in the real world. We’ll talk about the main types of network topologies, like bus topology, which is simple, and mesh topology, which is strong. We’ll also talk about their pros and cons and how they are used in real life. Expect clear explanations, visual aids like network topology diagrams, and real-world examples to make the subject easy to understand and useful. Let’s get going!
What Is Network Topology?
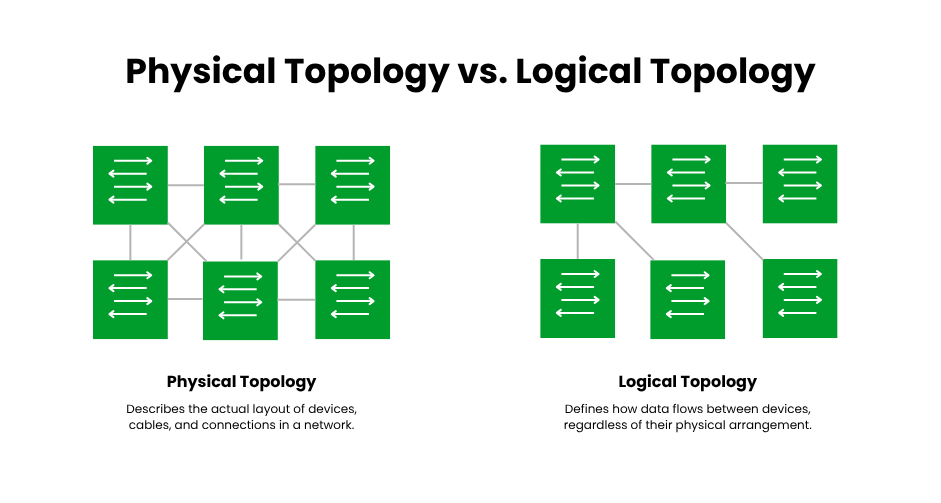
Network topology is the way a network is set up, including how devices (nodes) and connections (links) are arranged. It can be physical, like the actual cables, switches, or wireless connections, or logical, which is more about how data moves through the network, no matter how it is set up. A physical star topology could look like devices radiating out from a central hub, while a logical star topology could look like a ring if data flows in a circle.
The idea is very important to computer networking because it affects how devices talk to each other. The topology of a network, whether it’s a small home Wi-Fi network or a large corporate WAN, affects how well it works, how fault-tolerant it is, and how easy it is to add more devices. Knowing what network topology is and the different types of it is the first step to designing or fixing networks well.
Importance of Networking
Why does network topology matter? The topology directly affects a network’s performance. A well-chosen topology ensures fast data transfer, minimizes downtime, and simplifies maintenance. If your network ever experiences slow performance or frequent disconnections, check out our detailed guide on how to troubleshoot common network issues for practical solutions. For instance, a topology with a single point of failure, like a bus, can cripple a network if the main cable fails. Conversely, a mesh topology offers redundancy, keeping the network operational even if one connection breaks.
Cost and complexity are also influenced by network topology. While complex topologies like mesh are perfect for critical systems, but cost more; simpler configurations like bus or star topologies are more affordable for small networks. IT workers must balance performance requirements, financial constraints, and future expansion when choosing a topology.
Key Characteristics
Key factors in evaluating topologies include:
- Scalability: Can the network grow easily?
- Cost: How much cabling or equipment is needed?
- Reliability: Does the network stay up if a component fails?
- Maintenance: Is it easy to troubleshoot or expand?
We’ll go into more detail about these features in the next section on network topology types.
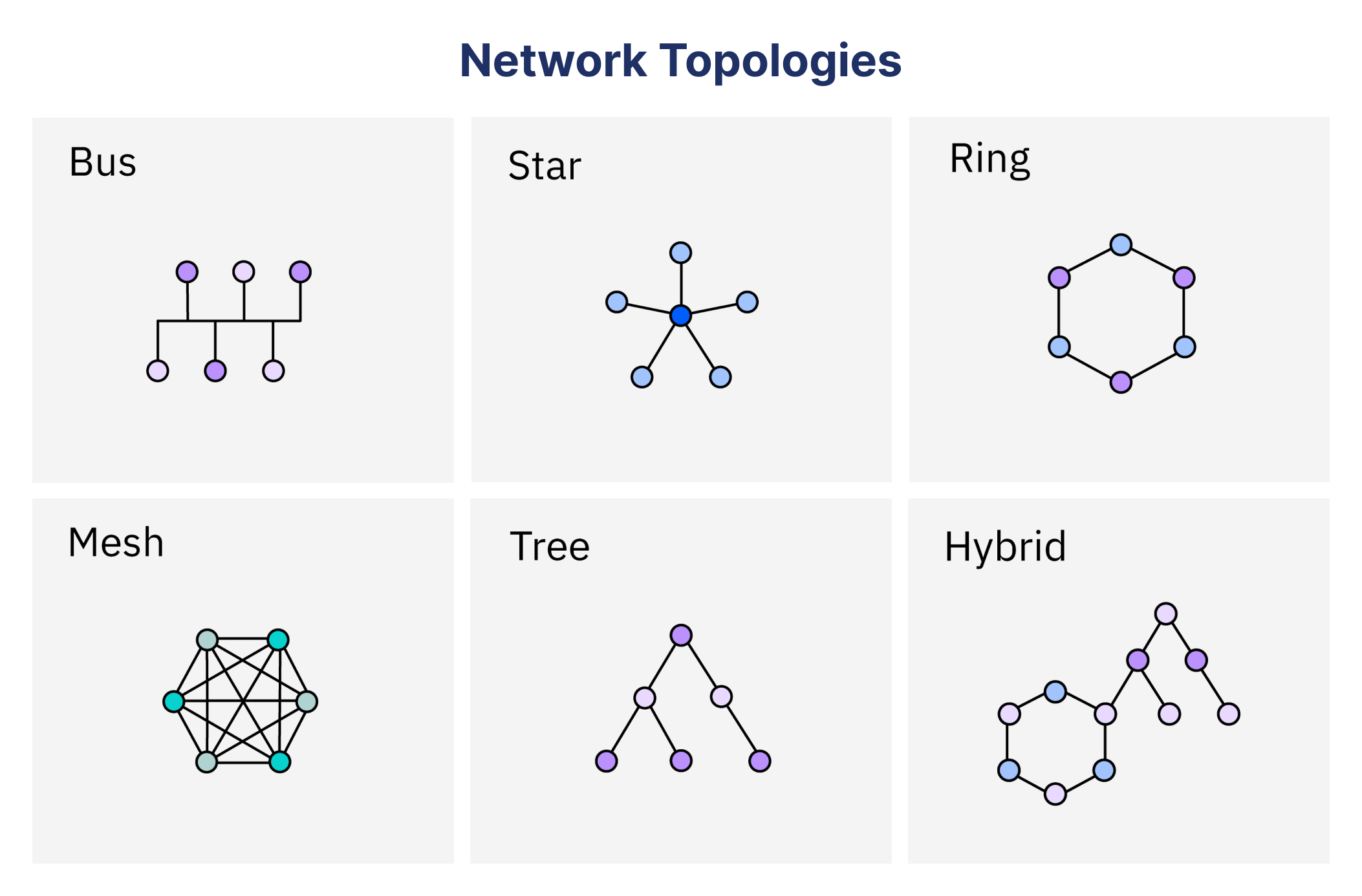
Types of Network Topology
There are various types of network topologies, each with its own structure and applications. Point-to-point, bus, ring, star, mesh, tree, and hybrid are the primary varieties. From small home networks to massive enterprise systems, each topology works well in a variety of situations. Knowing the different kinds of network topologies makes it easier to balance cost, performance, and dependability when choosing the one that best suits a given set of requirements.
The structure, benefits, drawbacks, and examples of each type are examined below, with a particular emphasis on bus, star, and mesh topologies in accordance with the keyword focus.
Point-to-Point Topology
Using a single link, like a point-to-point wireless bridge or a dedicated fiber optic cable, point-to-point topology creates a direct connection between two devices. It is the most basic network structure, providing high bandwidth and low latency (usually less than 1 ms for direct fiber links), which makes it perfect for situations that call for quick, continuous communication. Point-to-point connections are still utilized in contemporary leased lines and were utilized in early telecommunications, such as analog phone lines.
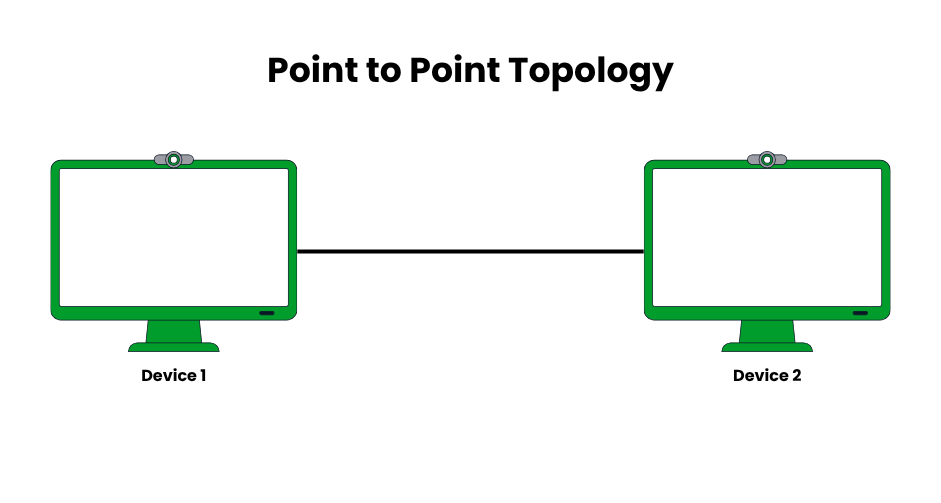
- Pros: Simple setup, minimal hardware (e.g., two routers), high-speed data transfer (up to 10 Gbps in fiber links), and low latency. No need for complex routing protocols.
- Cons: Limited to two nodes, making it unscalable for multi-device networks. Adding more nodes requires additional direct links, increasing costs.
- Examples: A leased line connecting two corporate offices for secure data transfer, or a point-to-point wireless link between two buildings in a campus network.
- Implementation Tips: Use for high-priority connections, like disaster recovery sites. Ensure link redundancy with failover mechanisms (e.g., dual leased lines).
- Modern Relevance: Common in WAN connections (e.g., MPLS circuits) and 5G backhaul links between cell towers.
Bus Topology
In a bus topology, every device is connected to the backbone, which is a single shared communication medium that is usually an Ethernet or coaxial cable. Only the intended recipient processes the data, even though it is broadcast to all devices. Although bus topology, which was popular in the 1980s with early Ethernet (e.g., 10BASE5), has mostly been replaced by star topology because of performance issues, it is still studied for its historical significance.
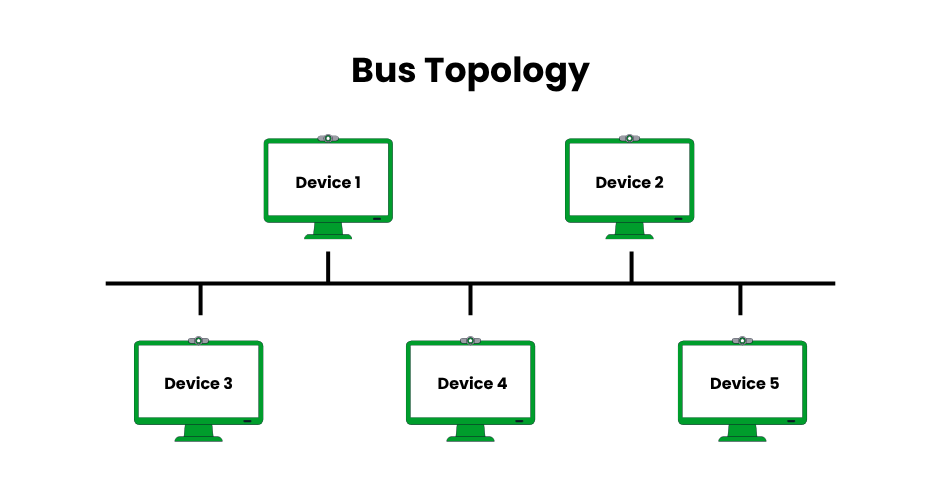
- Pros: Cost-effective, requiring minimal cabling (e.g., one coaxial cable vs. multiple fiber stars). Simple to install, ideal for small, budget-constrained networks.
- Cons: A single cable failure halts the entire network. Data collisions occur in busy networks, reducing throughput (e.g., 10 Mbps shared in early Ethernet). Limited scalability due to signal degradation over long distances.
- Examples: Older LANs like 10BASE5 Ethernet in small offices, or temporary setups for low-cost networks.
- Implementation Tips: Use terminators at cable ends to prevent signal reflection. Monitor for collisions using tools like Wireshark. Suitable only for small networks (<10 devices).
- Modern Relevance: Rarely used today but seen in niche applications like certain industrial control systems with shared bus protocols (e.g., CAN bus).
Ring Topology
Each device is connected to the next via ring topology, creating a closed loop in which data flows in a single direction (or both directions in dual-ring configurations). To stop degradation, each node boosts the signal by acting as a repeater. This topology, which was made popular by IBM’s Token Ring in the 1980s, employs a token-passing protocol to prevent data collisions and guarantee consistent performance.
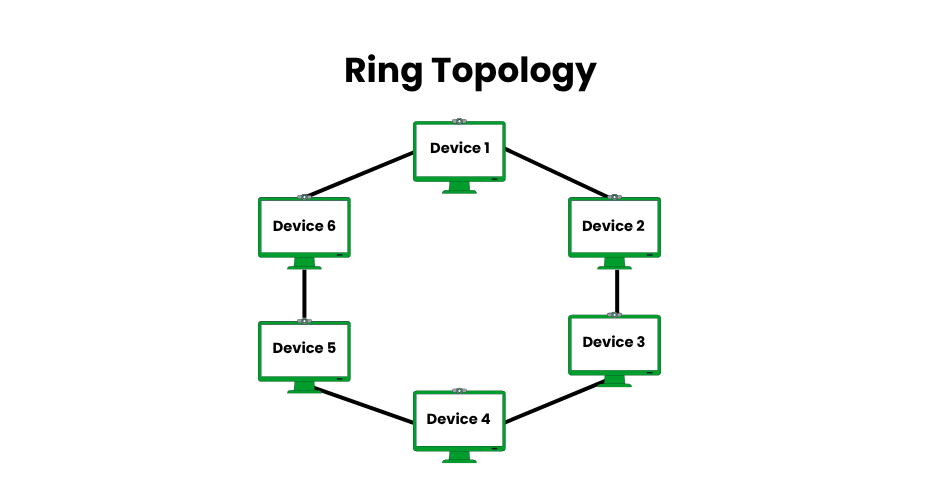
- Pros: No data collisions, offering stable performance (e.g., 16 Mbps in Token Ring). Efficient for small to medium networks with consistent traffic.
- Cons: A single node or cable failure disrupts the entire network unless dual rings are used. Adding/removing nodes requires reconfiguring the loop, complicating maintenance.
- Examples: Legacy Token Ring networks in offices or metro Ethernet rings in telecommunications for regional connectivity.
- Implementation Tips: Use dual-ring setups (e.g., FDDI) for redundancy. Monitor node health to prevent loop breaks. Best for networks with stable device counts.
- Modern Relevance: Seen in metro networks and some industrial systems (e.g., PROFIBUS), but largely replaced by Ethernet-based star or mesh topologies.
Star Topology
All devices are connected to a central hub or switch via star topology, which controls data flow. It is very dependable and simple to handle because even if one cable or device fails, the others continue to function. Due to the extensive use of Ethernet switches and Wi-Fi routers, it is the most popular topology in contemporary networks.
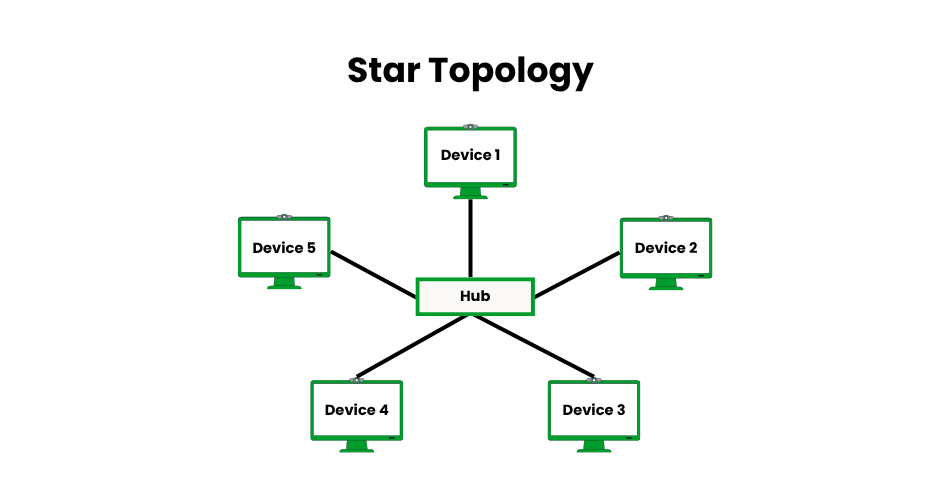
- Pros: Easy to manage and troubleshoot; device failures are isolated. Scalable, as new devices can be added to the hub (up to port limits, e.g., 48 ports on a switch). High reliability with no network-wide failures unless the hub fails.
- Cons: The central hub (e.g., switch or router) is a single point of failure. Requires more cabling than bus topology, increasing costs (e.g., 100 meters of Ethernet cable per device).
- Examples: Home Wi-Fi networks with devices connected to a router, or office LANs with computers linked to an Ethernet switch.
- Implementation Tips: Use managed switches for advanced features like VLANs. Ensure the hub has sufficient bandwidth (e.g., 1 Gbps ports) to avoid bottlenecks. Consider redundant hubs for critical networks.
- Modern Relevance: Dominant in LANs, Wi-Fi networks, and small business setups due to its simplicity and compatibility with modern Ethernet standards (e.g., 802.3).
Mesh Topology
Devices can be directly connected to numerous other devices using mesh topology, either fully (every node to every other) or partially (selective connections). While partial mesh strikes a balance between cost and reliability, full mesh provides maximum redundancy because data can follow multiple paths. Although it necessitates substantial infrastructure, it is perfect for high-availability systems.
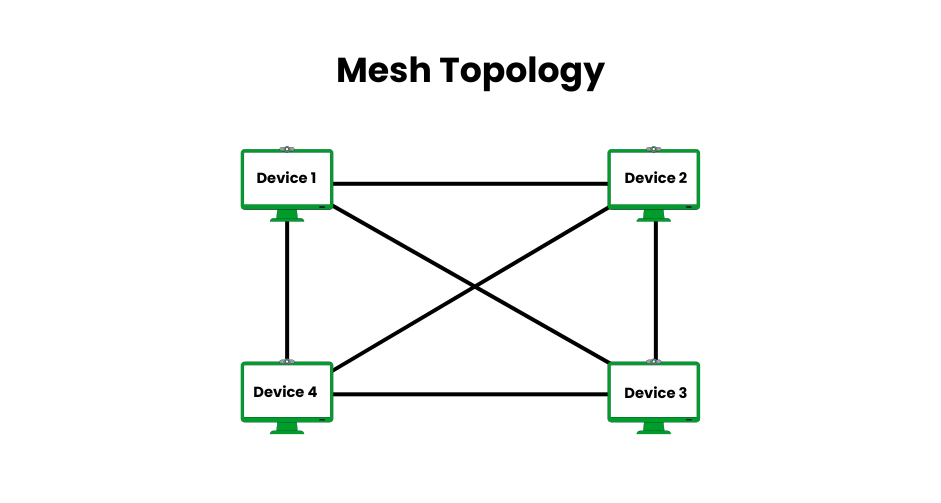
- Pros: Extremely reliable; multiple paths ensure data delivery (e.g., 99.999% uptime in full mesh). High bandwidth potential with dedicated links (e.g., 10 Gbps per connection). Fault-tolerant, as link failures reroute traffic.
- Cons: Expensive due to extensive cabling or wireless setup (e.g., N*(N-1)/2 links for N nodes in a full mesh). Complex to configure and maintain, requiring advanced routing protocols.
- Examples: Internet backbone with interconnected routers, wireless mesh networks in smart cities, or data center fabrics for cloud computing.
- Implementation Tips: Use a partial mesh for cost efficiency in less critical areas. Employ dynamic routing protocols (e.g., OSPF) for efficient path selection. Ideal for IoT or 5G networks requiring redundancy.
- Modern Relevance: Critical in data centers, cloud infrastructure, and IoT networks. Wireless mesh is growing with 5G and smart city deployments.
Tree and Hybrid Topologies
Devices are arranged hierarchically using tree topology, with bus-like backbones (roots) connecting star-configured groups (branches). Because branches can be added without affecting the core, it is scalable for large networks. For specialized performance, hybrid topology blends several topologies, like star-mesh or star-bus.
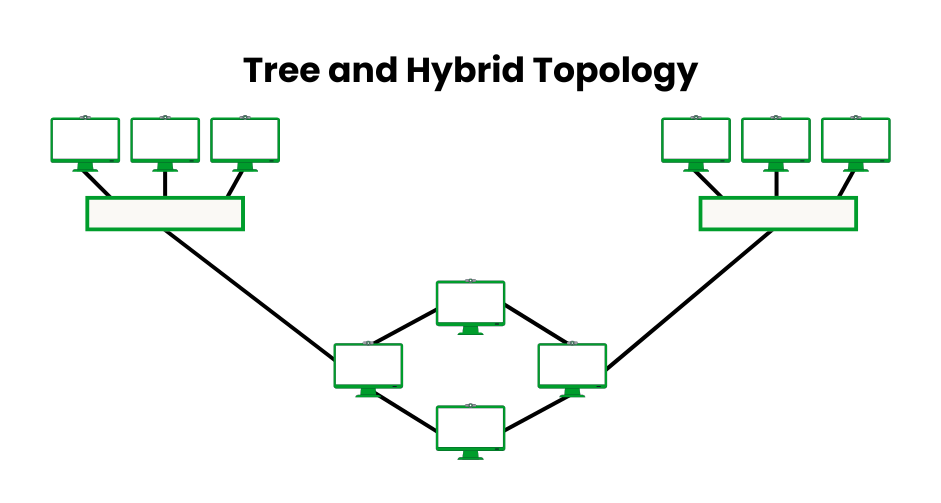
- Pros: Tree is highly scalable, supporting large networks (e.g., thousands of devices in campus setups). Hybrid offers flexibility to tailor performance, combining redundancy and cost efficiency.
- Cons: The Tree relies on the root node; a backbone failure affects all branches. Hybrid topologies are complex to design and troubleshoot, requiring skilled management.
- Examples: Tree in university campus networks with departmental LANs linked to a central backbone; hybrid in enterprise WANs combining star (branch offices) and mesh (data centers).
- Implementation Tips: Use redundant backbones in tree topologies to avoid single-point failures. For hybrids, document configurations clearly to simplify maintenance. Suitable for large, structured networks.
- Modern Relevance: Trees are common in campus or enterprise settings; hybrid is prevalent in cloud-integrated networks, combining on-premises and remote infrastructure.
Comparison Table of Topology
| Topology | Structure | Pros | Cons | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point-to-Point | Direct link between two nodes | Simple, fast | Not scalable | Server-to-server links |
| Bus | Single shared cable | Cost-effective, easy setup | Single failure crashes network | Early Ethernet LANs |
| Ring | Circular loop | No collisions, efficient | Node failure disrupts network | Token Ring, metro networks |
| Star | Central hub connecting all nodes | Easy to manage, fault isolation | Hub failure affects all | Home Wi-Fi networks |
| Mesh | Multiple direct connections | High redundancy, reliable | Expensive, complex | Internet backbone, smart cities |
| Tree | Hierarchical star-bus structure | Scalable, organized | Root failure impacts branches | Campus networks |
| Hybrid | Combines multiple topologies | Flexible, customizable | Complex to design | Enterprise WANs |
What Are Network Topology Diagrams?
Network topology diagrams, which display nodes (devices) and links (connections), are graphic depictions of a network’s structure. Network planning, troubleshooting, and documentation all depend on these diagrams. They support IT workers in planning expansions, identifying bottlenecks, and visualizing data flow. A star topology diagram, for instance, makes it simple to identify the critical hub because it clearly displays a central hub with radiating devices.
How to Create Diagrams
Creating a network topology diagram involves:
- Identify Devices: List all nodes (e.g., computers, routers, switches).
- Map Connections: Define how devices are linked (e.g., Ethernet cables, wireless).
- Choose a Tool: Use software like Microsoft Visio, SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper, or Lucidchart for professional diagrams.
- Label and Organize: Clearly label devices and connections for clarity.
These tools allow manual design for planning purposes or automatically generate diagrams by scanning networks. Diagrams are particularly helpful for illustrating complicated configurations, such as hybrid topologies.
Examples of Diagrams
- Bus Topology Diagram: Shows a single cable with devices attached, like a legacy Ethernet LAN.
- Star Topology Diagram: Illustrates a router with connected devices, common in home networks.
- Mesh Topology Diagram: Displays multiple interconnections, typical in data centers.
Real-World Examples and Applications
Home and Small Office Networks
Star topology dominates home and small office networks due to its simplicity and reliability. In a typical setup, devices like laptops, smartphones, and smart TVs connect to a central Wi-Fi router. If one device fails, others continue functioning, making it ideal for non-critical environments. For example, a home network with a router supporting 10 devices uses a star topology for easy setup and management. If you’re planning to build your own setup at home or in a small office, check out our tutorial on how to set up a home server to make your network more secure and efficient.
Enterprise and Campus Networks
Tree or hybrid topologies are frequently used by large organizations. A tree topology, which is perfect for corporate campuses or universities, links several star-configured departments with a central backbone. Enterprise WANs frequently use hybrid topologies, such as a star-bus combination, in which branch offices (star) are connected to the headquarters backbone (bus). Scalability and flexibility are balanced in these configurations.
Specialized Networks
In high-reliability settings, such as data centers or smart cities, where numerous connections guarantee that no single failure interrupts service, mesh topology excels. In urban areas, for example, wireless mesh networks enable devices to relay data, ensuring connectivity. Even though it’s less popular now, bus topology was utilized in older systems, such as the first LANs with coaxial cables.
Consider the traffic control system in a smart city that uses mesh topology to provide redundant sensor connections.
Choosing the Right Topology
Selecting a network topology depends on several factors:
- Cost: Bus and star are budget-friendly; mesh is costly due to cabling.
- Scalability: Tree and hybrid topologies suit growing networks.
- Reliability: Mesh offers redundancy; bus and ring are prone to single-point failures.
- Maintenance: Star is easy to troubleshoot; mesh is complex.
For small offices, star topology is often the best choice due to its simplicity. Critical systems like data centers prefer mesh for reliability.
Modern Trends
Topology decisions are influenced by contemporary networking trends. Because wireless technologies lessen the need for physical cabling, Wi-Fi and Internet of Things networks are increasingly using star and mesh topologies. By introducing virtual topologies, Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN) enables dynamic reconfiguration without requiring changes to physical layouts. Cloud-based systems are increasingly using hybrid topologies, which combine global mesh connections with local star networks.
Conclusion
Any computer network’s foundation is its network topology, which specifies how devices connect and exchange information. Every type of topology has a specific purpose, ranging from the economical bus topology to the dependable mesh topology and flexible star topology. These ideas are brought to life through network topology diagrams and practical examples, such as home Wi-Fi or business WANs. Knowledge of network topology types enables novices, IT specialists, and students to create dependable, scalable, and effective networks.
FAQs
1. What is the simplest type of network topology?
Point-to-point, the most basic network topology, uses a single link, like a leased line, to directly connect two devices. It is perfect for dedicated connections like office links or 5G backhaul because it is quick, low-latency, and simple to set up.
2. Why use a network topology diagram?
IT workers can plan, troubleshoot, and identify problems like bottlenecks or misconfigurations with the aid of a network topology diagram, which graphically maps devices and connections. Complex configurations, like hybrid networks, are simpler to comprehend and administer with the use of programs like Visio or SolarWinds.
3. Which network topology is best for small businesses?
Because of its ease of scalability, simplicity, and dependability, star topology is ideal for small businesses. By connecting to a central hub or router, devices isolate failures for seamless operation and reduce setup costs.
4. How does mesh topology improve reliability?
By providing redundant paths between several devices and enabling data to reroute automatically in the event of a link failure, mesh topology increases reliability. Despite being expensive, it guarantees high uptime and is perfect for vital systems like IoT networks and data centers.
5. What are the limitations of bus topology?
Bus topology has a single point of failure, meaning that the network will stop working if the main cable breaks. Despite its low cost, it is not appropriate for large networks due to data collisions and signal loss, which limit scalability and reduce performance.

Let's Start Your Project
Get free consultation for your digital product idea to turn it into reality!
Get StartedRelated Blog & Articles

Netizens
May 29, 2024
What Must an Entrepreneur Do After Creating a Business Plan?
Congratulations! You've poured your heart and soul into crafting a stellar business plan. It outlines your

Netizens
April 26, 2024
Best Accounting Software for Pharmaceutical
The pharmaceutical industry is a complex one, with strict regulations and a constant need for efficient

Netizens
December 5, 2024
How IT Solutions Are Transforming the Pharmacy Industry
The pharmacy industry is undergoing a revolution, powered by cutting-edge IT solutions. From improving patient care




