This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Edge Computing and Its Impact on Data Centers
Data is the most valuable asset to businesses in the modern market. The rising popularity of IoT, AI, and 5G creates the need for better data processing. Not only should it be low latency, but it must be cost-efficient and in real-time.
Although data centers have been the norm, edge computing is a new solution. It brings data processing to its source, providing benefits.
This blog looks at edge computing and its impact on data centers, benefits, and challenges.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is the practice of storing and processing data closer to the source. In this data distribution model, data isn’t sent far away to off-site data centers. Instead, it lets devices, sensors, and local servers manage computing on-site.
The most appealing benefit of this is faster processing and less bandwidth use. This computing approach is in demand for its perks, and we’ll explain how this affects data centers.
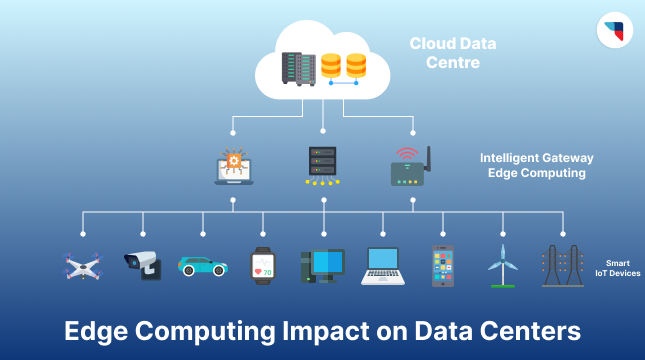
How Does Edge Computing Impact Data Centers?
Edge computing won’t replace data centers, as it fulfills the capabilities they lack. Instead, it will influence changes in data centers, and these are a few of them:
1. Changing Data Center Design
Data center designs will change according to data processing and storage requirements.
- Data center size will decrease as enterprises choose a computing platform over other options.
- Demand for modern, energy-efficient hardware will increase to support distributed deployments.
2. Reduced Latency & Bandwidth Requirements
Edge computing placement enables the optimization of network resources and reduces response times.
- Data processing is closer to the source, data travels less, allowing faster responses.
- Edge computing allows devices to function on a weak or absent internet connection. It reduces internet dependence, which is crucial for applications in remote locations.
3. Spreading of Security & Privacy Threats
Local data processing helps in ensuring data compliance and sovereignty. That means, data stays within the same region as its source.
- Choosing local data processing helps keep sensitive data nearby, within the same region.
- One drawback is that it provides many entry points for threats and security issues. Whereas data centers are more secure with fewer locations.
4. Adjusting Workload Distribution
Combining edge and centralized data centers can provide an advanced solution for enterprises.
- An edge data center manages all time-sensitive processing, sending only relevant data forward.
- Centralized centers handle most of the workload, like long-term storage and AI training.
5. Decentralizing Base
Traditional data centers have a centralized design, meaning they serve vast regions together.
- Edge computing requires distribution, which means smaller “micro data centers” near users.
- This unique need can lower reliance on massive, centralized hubs for data storage.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Data centers handle excessive amounts of computing. They are centralized computing systems that store and process enormous amounts of data.
Governments, enterprises, and cloud server providers use these due to their cost-efficient nature. It reduces their IT workloads and costs for storing databases and supporting applications.
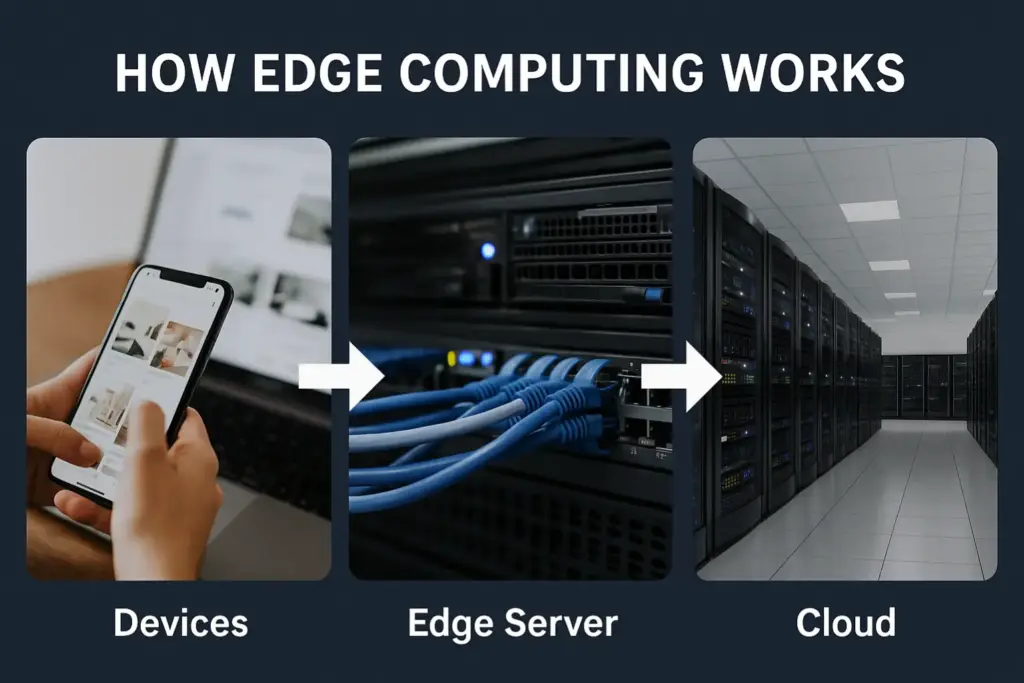
Working Mechanism of Edge Computing
- Data Generation – Machines, cameras, sensors, or any IoT device collect data.
- Local Processing – Data goes to nearby servers (edge centers) for real-time processing.
- Rapid Decision-Making – Based on the data, connected systems can act immediately.
- Selective Data Transfer – A summarized copy of data is sent to the cloud data center for long-term storage.
The biggest benefit of this system over others is the shorter distance for data to travel. It results in quicker responses and the ability to make decisions in real-time using data.
What are the Benefits of Using Edge Computing?
This computing model comes with benefits, helping companies streamline operations and lower costs.
- Real-time data processing
- Faster and accurate decision-making
- Lowers bandwidth costs
- Offline functionality reduces internet dependence
- Reduces latency and improves response speed
What are the Challenges of Using Edge Computing?
Although it has benefits, some challenges that edge computing brings are as follows:
- Security
This computing approach does create a few more security concerns than other cloud computing types. This is because of multiple entry points created from having devices and storage locations.
- Interoperability
Seamlessly integrating edge computing solutions is challenging. The lack of interoperability and standardization creates compatibility issues. Connecting IoT solutions with your preferred edge computing platform isn’t that easy.
- Implementation Costs
These systems are located near the client or even on-site. The costs can grow rapidly, making the setup impossible for some clients. In such cases, other options need consideration to reduce costs.
- Resource Limitations
Edge devices aren’t able to hold enough power, memory, and storage. This creates an issue for applications and services that require more resources.
Connection Between IoT and Edge Computing
Edge computing doesn’t send data far for processing. Instead, it chooses to bring processing closer to the data’s source.
Sensors, cameras, and other devices part of the Internet of Things (IoT) are central to this. They collect data, which is processed locally on edge devices.
It eliminates the need to send all raw data to the cloud. Sending all the data is slow and takes more bandwidth. Edge processing allows for quicker decision-making using immediate data.
IoT is central to this system, as these devices constantly collect data. Edge computing allows for quick and efficient data processing, sending vital data to the cloud.
Difference Between Edge and Cloud Computing
Edge computing holds a crucial role in the future of Cloud Computing with its advanced capabilities. But here are some differences that show why you need to choose one of them:
Real Life Edge Computing Use Cases
Edge computing is already in use, in some cases, without us knowing it.
IoT Applications
The Internet of Things (IoT) uses various devices to collect data. This data collection occurs daily and is necessary for real-time analytics.
Healthcare experts prescribe wearable monitors for data on heart rate and glucose levels. It lets them monitor any irregularities in heart rate or glucose levels.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving vehicles have various sensors to track data on obstacles, terrain, and routes. Edge computing allows for the processing of this data in real time. It allows vehicles to take instant actions like braking and turning.
Manufacturing & Industrial IoT (IIoT)
IoT devices also find use in the manufacturing industry, particularly in factories. Machines self-monitor and detect problems before they break down. This lowers the amount of downtime and reduces costs from these issues.
Smart Cities
Cities use sensors to collect data from and control traffic lights and surveillance cameras. They use the data to make real-time traffic light changes that prevent accidents and ease congestion.
Conclusion
When comparing cloud computing and edge computing, you’ll find that the latter has benefits. This alternative lets firms benefit from better latency and bandwidth. These two features enable resource saving and improve decision-making in real time.
Given these benefits, data centers will evolve to meet the needs of businesses that choose edge computing. Given these benefits, data centers will evolve to meet the needs of businesses that choose edge computing. To explore more about enterprise solutions, check out Netizens Technologies’ software development services
FAQs
1. What is one of the main challenges of edge computing?
A crucial challenge of edge computing is its scalability and interoperability issues. It’s still difficult to integrate edge platforms with IoT solutions with ease.
2. Is edge computing better than cloud computing?
Making this decision will depend on your exact situation and requirements. Edge computing collects, transfers, and processes data quickly and in real-time. Cloud computing is best for scalability, and when you lack enough resources.
3. What are the security issues with edge computing?
This form of computing creates more access points for potential threats.
4. What is the most significant impact of edge computing?
This computing allows for real-time data processing and constant data collection.
5. What is edge computing with an example?
Edge computing is a decentralized model, bringing data processing to the source. An example of how it works is wearable health monitors that track and collect daily heart rate readings.
6. What is the difference between a data center and an edge data center?
A data center is a centralized data computing facility serving a wide area. An edge data center is a decentralized, mini data center.

Let's Start Your Project
Get free consultation for your digital product idea to turn it into reality!
Get Started




